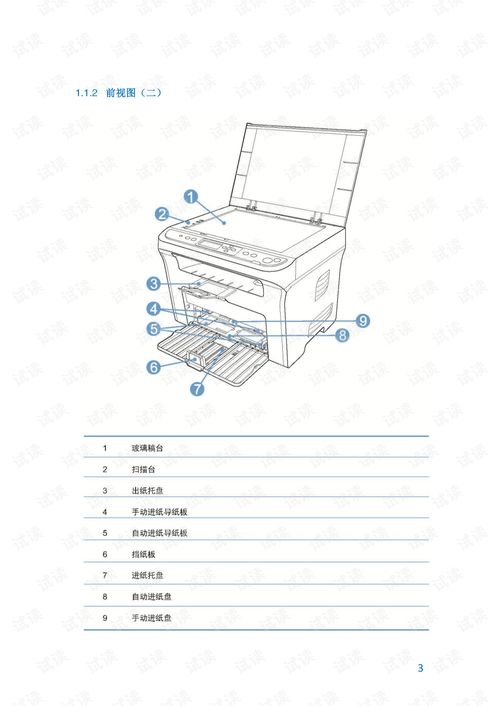
Title: Comprehensive Guide to Architectural Design
4. Aesthetic Considerations
Establishing clear communication and understanding with the client is essential throughout the design process. Architects should actively involve clients in decisionmaking, listen to their preferences and concerns, and provide expert guidance to translate their vision into reality.
5. Sustainable Practices
With increasing emphasis on environmental responsibility, architects integrate sustainable design principles into their projects. This includes strategies such as passive solar design, energyefficient systems, water conservation measures, and use of ecofriendly materials. Sustainable architecture aims to minimize environmental impact and promote longterm resource efficiency.
1. Concept Development
Architecture should respond sensitively to its cultural, historical, and environmental context. By studying the context, architects can create designs that harmonize with the surroundings, respect local traditions, and contribute positively to the built environment.
Integrating sustainability into architectural design is no longer optional but imperative. Architects should strive to incorporate energyefficient strategies, renewable resources, and environmentally conscious design principles into their projects to minimize carbon footprint and promote ecological resilience.
1. Client Collaboration
3. UserCentered Design
The design process typically begins with conceptualizing ideas based on the client's requirements, site constraints, and architectural principles. Architects explore various concepts through sketches, models, and digital renderings to visualize the potential form and function of the building.
2. Contextual Response
Ensuring structural stability and safety is fundamental in architectural design. Architects collaborate with structural engineers to develop robust structural systems that can withstand various loads and environmental conditions. Structural considerations influence design decisions related to building form, material selection, and construction methods.
This comprehensive guide provides insights into the intricacies of architectural design, from conceptualization to execution, and offers practical guidelines for architects to create meaningful and impactful built environments.
6. Continuous Learning
3. Functional Planning
2. Site Analysis
Architectural design is a collaborative endeavor that melds artistic vision, technical expertise, and social responsibility to create built environments that enrich lives and inspire communities. By embracing innovation, sustainability, and usercentered design principles, architects have the power to shape a more inclusive, resilient, and beautiful world.
5. Structural Integrity
Architectural design thrives on innovation and creativity. Architects are encouraged to explore unconventional ideas, experiment with new technologies, and push the boundaries of traditional design conventions. Embracing innovation fosters unique, inspiring architectural solutions.
Architects develop functional layouts that optimize the use of space while accommodating the needs of occupants. This involves programming different areas within the building, considering circulation flow, accessibility requirements, and zoning regulations. A welldesigned floor plan enhances efficiency and user experience.
4. Innovation and Creativity
Designing for the endusers' needs and preferences enhances the functionality and usability of the built environment. Architects should conduct user research, anticipate future requirements, and prioritize humancentric design solutions that prioritize comfort, accessibility, and wellbeing.
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the architectural design process. Architects utilize Building Information Modeling (BIM), computeraided design (CAD) software, and parametric modeling tools to create, analyze, and refine their designs with precision. Digital technologies enhance collaboration, visualization, and project coordination.
Architectural design is a multifaceted discipline that encompasses the planning, designing, and construction of buildings and structures. It involves a combination of artistic vision, technical expertise, and practical considerations to create spaces that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. Whether it's designing a residential home, commercial complex, or public space, architects play a crucial role in shaping the built environment.
6. Environmental Sustainability
Architectural design is as much about aesthetics as it is about functionality. Architects carefully select materials, forms, and architectural styles to create visually appealing structures that resonate with the project's purpose and context. Attention to detail in elements such as façade design, fenestration, and landscaping contributes to the overall architectural expression.
Architecture is a dynamic field that evolves with changing societal needs, technological advancements, and design trends. Architects should engage in lifelong learning, attend professional development courses, and stay abreast of industry best practices to enhance their skills and deliver highquality designs.
Understanding the site conditions is essential for effective architectural design. Site analysis involves evaluating factors such as topography, climate, orientation, and surrounding context. This information influences design decisions regarding building placement, spatial organization, and sustainable design strategies.